Everyone is looking for attractive investments in this finance world. However, finding out the feasibility of the investment or business project is a monumental challenge for investors. Want to learn how to find the attractiveness of your investments?
Today, we learn about the two most reliable financial metrics and their differences – CAGR and IRR. Both are popular financial metrics and are widely used in financial models. In addition, these metrics help investors to:
- Forecast the investment returns
- Compare different investment or business models
- Analysis of past performances
You may have come across some popular phrases such as what is CAGR in mutual fund, what is CAGR in stock market, what is the IRR of this investment scheme, and more. So, let’s delve deep to learn about the meaning of IRR and CAGR, their differences, how they work, which is the better option for evaluation and in which scheme, and so on!
What is Compound Annual Growth Rate?
The compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) is a financial metric to measure the annual growth of investment over time. It evaluates the returns on investment you have earned or going to earn during a specific period, with the impact of compounding taken into consideration.
CAGR is a reliable method for calculating the rise and fall of your ROI. It is also incredibly effective in measuring the expected future returns or comparing past performance.
Investment or investment portfolio witnesses standard fluctuation over the period due to market volatility. For example, your investment might see a smaller gain in one year, a huge gain in the next year, and a slim loss in the following year. This cycle continues with different rates of returns throughout the period.
How To Calculate CAGR?
The calculation of CAGR is simple. It principally considers the initial and final investment made during the period. The compound annual growth rate formula is as follows:
CAGR = (Final Value/ Initial Value)^1/n – 1
Here,
Final value = The ultimate Value at the end of the investment.
Initial Value = Original value at the beginning of the investment
N = It represents the number of years of investment
Let us understand the CAGR calculation more clearly with an example,
Suppose X invests ₹20,000 in the shares of a company for five years. After maturity, X cashed out the investments for ₹30,000. The CAGR of your investment is:
CAGR = {(30,000/20,000)^ 1/5 – 1} = 8.45%
It means the original investment of X ₹20,000 generated returns of 8.45% over a five-year period, which is equal to ₹30,000 at maturity.
What is IRR?
IRR full form is Internal Rate of Return. It is a financial metric used to measure the profitability of a project, business, or investment. In other words, IRR is a discount rate at which the NPV (Net Present Value) of a project or investment is zero.
IRR excludes all the external factors such as capital costs, inflation, tax, financial risks, and other inputs; that’s why it is called the internal rate of return. That means the net cash flows, i.e., cash inflows and cash outflows, would be equal to 0.
The internal rate of return method is a great way to assess the attractiveness of a project or investment. It gives estimates of the future value of an investment, allowing investors to analyze investment risks and make prudent decisions.
With the help of IRR, business owners or investors can estimate which projects or investments have the better potential cash outflow. Higher the IRR, the better the investment opportunity.
How to Calculate IRR?
Before we figure out the IRR formula, it is interesting that no one spends time calculating IRR manually. Calculating IRR by hand is a hectic process and time-consuming. Instead, most people use computing software, Spreadsheet or MS Excel, to calculate IRR within seconds. To calculate IRR, we need to derive NPV (Net Present Value).
NPV is the net difference between cash inflows and cash outflows in a specific period.
NPV Formula,
NPV = Cash flow/ (1 + i)t – initial investment
Where,
i = discount rate or required rate
t = time period
Cash flow = net cash flow during a specific investment period
Initial investment = original or the first investment of the project
Now, let’s understand the Internal Rate of Return Formula:
IRR Formula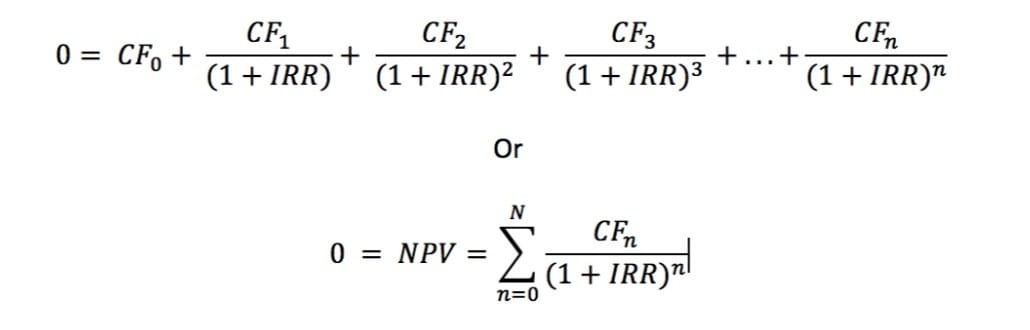
Where,
CF0 = Original/ Initial investment
CF1, CF2, CF3, CF4, …. CFn = Cash flows
n = each single period
N = Investment period
NPV = Net Present Value (here NPV is equal to zero)
IRR = Internal Rate of Return
Here is a numerical example,
Suppose X invested ₹20,000 and for three years, she received returns of ₹5,000, ₹8000, and ₹10,000, respectively. The expanded IRR computation as follows:
NPV = CF0 + CF1/ (1 + IRR)1 + CF2/(1 + IRR)2 + CF3/ (1+IRR)3
0= (₹20,000) + ₹5,000/ (1 + IRR)1 + ₹8000/ (1 + IRR)2 + ₹10,000/(1+IRR)3
As we see, it is nearly impossible to calculate the IRR manually. We could try solving it through a hit-and-trial method, which will consume a lot of time. For ease, saving time, and getting accurate results, most investors use Excel or Spreadsheet to calculate the IRR of the intended investment. Let’s calculate the IRR of the following investment using Excel:
Step 1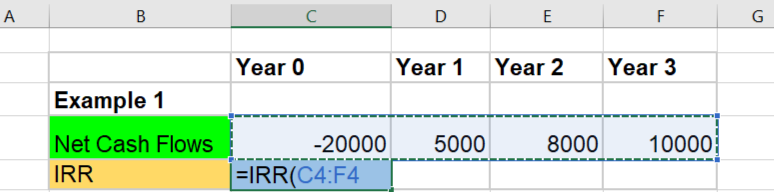
Step2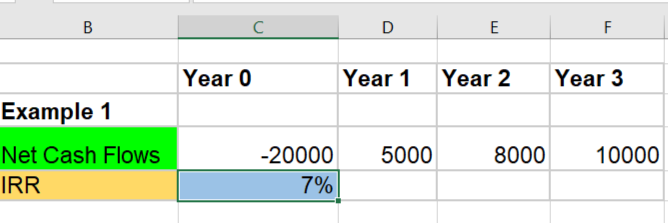
The process is simple. Just scribble down net cash flows year-wise and run the IRR equation. The IRR of this investment is 7%. So, the higher the IRR, the better the investment.
CAGR vs. IRR: What’s the Difference?
CAGR and IRR are standard financial metrics to measure expected return on investment. Each metric has its own relevance, depending on the investment structures.
Let’s check out some fundamental differences between IRR vs CAGR:
Ease of Calculation
The method of CAGR is relatively much easier to calculate and understand than IRR. It needs only a few essential inputs to derive the rate of return, such as initial investment, final value, and investment period.
IRR is a complex metric involving many inputs and complicated methods. As a result, it isn’t easy to calculate manually. Mostly, IRR is calculated using software, Excel, or a Spreadsheet to save time and get better results.
Diverse Investment Avenues
CAGR is beneficial, where no cash inflows and outflows are involved. In such types of investments, it is a perfect metric that will help investors to decide where to invest and which will be better options.
When there are variations in returns or the investment depends on market volatility, the IRR is an excellent option. It considers net cash flows during the period, offering a better picture of investment over a specific period.
Usage and Purpose
CAGR is primarily used for analyzing past performances of investments, i.e., stocks and mutual funds. It gives a single compound rate of growth of an investment. CAGR is best for calculating lump sum investment.
On the other hand, the IRR is used to make a fair comparison between different investment schemes. Its primary purpose is to forecast investment returns rather than analyze and evaluate historic returns. IRR is good for taking capital budgeting decisions.
Time Value of Money
The time value of money plays a pivotal role in any business segment, project, and other investments. It provides a better overview of capital expenditure.
CAGR ignores the movement of cash and the time value of money during the investment period. So, it doesn’t present an accurate investment worth.
IRR is a preferable option for forecasting investment returns, considering the time value of money. It gives a realistic outlook and helps investors to make prudent decisions, comparing the different projects.
The Bottom line
After understanding the concept and differences, a question arises – Which is better: CAGR vs. IRR? Depending on the investment prospects, each method has its own significance and purpose.
In the financial industry, IRR gives a more realistic picture than CAGR while assessing investments and business projects. Therefore, it has broader appeal among investors as the method takes account of the realities of the financial circles and market volatility. In some cases, CAGR serves the purpose in an optimum way..

Leave a Reply